How blockchain works
🔗 Process of Blockchain: How It Works Step by Step
Explore the entire journey of a blockchain transaction — from digital authentication to final verification — and learn how it revolutionizes data transparency and security.
📘 Table of Contents
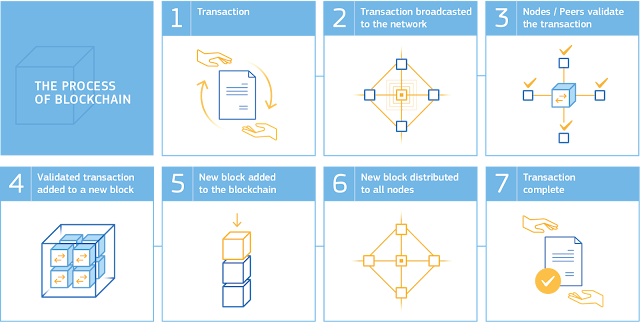
🔐 1. Transaction (Authentication)
Every blockchain transaction begins with authentication using cryptographic keys. Each user has:
- Private Key: Known only to the user and used to sign the transaction.
- Public Key: Shared with the network to verify authenticity.
📡 2. Transaction Broadcasted
After signing, the transaction is broadcast to a **peer-to-peer (P2P) network** of nodes. These nodes are individual computers or servers that maintain a copy of the blockchain ledger.
- Broadcasting allows **decentralization**, as no central authority is required.
- Nodes listen for new transactions and prepare them for validation by consensus.
🔎 3. Nodes Validate the Transaction
Validation is performed using a **consensus mechanism**, ensuring agreement among network participants that the transaction is valid. Common methods include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Requires nodes (miners) to solve a complex puzzle, ensuring time and effort are invested.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Relies on validators who "stake" coins to confirm transactions based on their holdings and trustworthiness.
📦 4. Validated Transaction to New Block
Once a transaction is verified, it is grouped with other validated transactions into a **block**. Each block contains:
- Data: A list of recent validated transactions.
- Hash: A unique identifier for the block.
- Previous Hash: Linking to the previous block for continuity.
🔗 5. New Block Added to Blockchain
Upon successful creation and validation, the block is **permanently added** to the blockchain:
- It becomes part of the ledger visible to all nodes.
- It’s **time-stamped** and immutable — no edits can be made after insertion.
- Each block connects to the next, forming a **tamper-proof chain**.
✅ 6. Transaction Complete
The transaction is now considered **final**. Every node in the network updates its copy of the blockchain to reflect the new block.
- This **distributed consensus** ensures trust without a central authority.
- Blockchain’s design allows **auditable and transparent records** accessible to all participants.
- The cycle repeats for every new transaction, maintaining a secure and efficient ecosystem.
🌍 Real-World Applications of Blockchain Process
- 💸 Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin, Ethereum — enabling peer-to-peer digital payments.
- 🏥 Healthcare: Securing patient records and preventing data breaches.
- 📦 Supply Chain: Tracking goods from origin to consumer with transparency.
- 📑 Smart Contracts: Self-executing agreements without intermediaries.
📚 Related Articles from Infokie
💬 Share Your Thoughts
What are your views on blockchain’s impact? Join the conversation in the comments below! 👇
